Our mission is to help neurology patients by best supporting their diagnosis and treatment. We are committed to providing you with fast and reliable CT imaging to make informed treatment decisions. They are, of course, particularly important in stroke, where time is brain. More than 6.5 million people die from stroke each year and more than 100 million people are currently living with the consequences of stroke, ranging from moderate to severe disability1.��
We firmly believe that innovation in computed tomography can create great momentum in neuroradiology and neurology. You think ahead in advancing neurology care. We innovate ahead with technologies that support you throughout the entire patient pathway. Discover how state-of-the-art CT technologies by Siemens Healthineers can help you care for your stroke patients.
Computed Tomography for NeurologyYou think ahead. We innovate ahead.
Clinical cases

CT role in head emergency and stroke assessment
Automated support along the imaging pathway
syngo.CT Dynamic Angio and syngo.CT Neuro DSA are part of the medical device syngo.CT Applications. Trauma Layouts, Stroke Layout, and Parallel Ranges are part of the medical device syngo.CT Extended functionalities. The products mentioned here are not commercially available in all countries. Due to regulatory reasons, their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Courtesy of Diagnostikum Graz, Austria
CTA of the head / neck including lung iodine map with NAEOTOM Alpha.Prime
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 13 mGy

Courtesy of Diagnostikum Graz, Austria
CTA of the head / neck with venous pathology with NAEOTOM Alpha.Prime
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 11.3 mGy
Courtesy of University Hospital Pilsen, Pilsen, Czech Republic
Head follow-up imaging after surgical procedure with NAEOTOM Alpha.Pro
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 50.9 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Follow-up patient after clipping with NAEOTOM Alpha.Peak
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 8.17 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 180 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital of Karolinska, Stockholm, Sweden
Quantum HD pediatric cochlear implant imaging with NAEOTOM Alpha.Peak
0.2mm | 120 kVp | CTDIvol 11 mGy

Courtesy of Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden
Head CT angiography with low-kV imaging
120 kV | 37 mAs | CTDIvol 40.1 mGy | ADMIRE
80 kV | 31 mAs | CTDIvol 14.6 mGy | ADMIRE

Courtesy of Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand
Triaging of intracranial hemorrhage patient supported by Mobile Stroke Unit (MSU)
120 kV | 33 mAs | CTDIvol 36.3 mGy | ADMIRE

Courtesy of Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden
Native head CT scan with intraventricular bleeding follow-up after trepanation
120 kV | 31 mAs | CTDIvol 34.29 mGy | ADMIRE

Courtesy of Hôpital Morges, Morges, Switzerland
Support stroke assessment with low kv imaging and zero-click thanks to Recon&GO
Native: 120kVp | CTDIvol 42 mGy – CTA 70kVp | CTDIvol 2.96 mGy – CT Perfusion 70kVp | CTDIvol 103 mGy

Courtesy of Hôpital Morges, Morges, Switzerland
Brain evaluation including spectral CTA of the cervical and cerebral vessels
CTA: 80 / Sn 140 kVp | CTDIvol 10.4 mGy Brain: 120 kVp | 40.4 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Visualization of iodine uptake with syngo.CT DE Brain Hemorrhage
TwinSpiral Dual Energy CT: 80/Sn150 KV | CTDIvol 37.06 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany
Ultra high-resolution inner ear without dose penalties thanks to Tin Filter
Sn130 kV | CTDIvol 24.07 mGy

Courtesy of Centro Hospitalar e Universitario de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Rule-out of bleeding and vascular status clarification
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 38.4 mGy | CTA: 80kV | CTDIvol 6.3 mGy

Courtesy of Paras Hospitals, Panchkula, India
Penumbra assessment with volume perfusion CT
Native: 120 kV | CTDIvol 37 mGy | CT Perfusion: 70kV | CTDIvol 162 mGy

CT role in head emergency and stroke assessment
Automated support along the imaging pathway
syngo.CT Dynamic Angio and syngo.CT Neuro DSA are part of the medical device syngo.CT Applications. Trauma Layouts, Stroke Layout, and Parallel Ranges are part of the medical device syngo.CT Extended functionalities. The products mentioned here are not commercially available in all countries. Due to regulatory reasons, their future availability cannot be guaranteed.

Courtesy of Diagnostikum Graz, Austria
CTA of the head / neck including lung iodine map with NAEOTOM Alpha.Prime
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 13 mGy

Courtesy of Diagnostikum Graz, Austria
CTA of the head / neck with venous pathology with NAEOTOM Alpha.Prime
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 11.3 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Pilsen, Pilsen, Czech Republic
Head follow-up imaging after surgical procedure with NAEOTOM Alpha.Pro
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 50.9 mGy

Courtesy of Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Follow-up patient after clipping with NAEOTOM Alpha.Peak
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 8.17 mGy | Perfusion: 70kVp | CTDIvol 180 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital of Karolinska, Stockholm, Sweden
Quantum HD pediatric cochlear implant imaging with NAEOTOM Alpha.Peak
0.2mm | 120 kVp | CTDIvol 11 mGy

Courtesy of Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden
Head CT angiography with low-kV imaging
120 kV | 37 mAs | CTDIvol 40.1 mGy | ADMIRE
80 kV | 31 mAs | CTDIvol 14.6 mGy | ADMIRE

Courtesy of Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand
Triaging of intracranial hemorrhage patient supported by Mobile Stroke Unit (MSU)
120 kV | 33 mAs | CTDIvol 36.3 mGy | ADMIRE

Courtesy of Skåne University Hospital, Lund, Sweden
Native head CT scan with intraventricular bleeding follow-up after trepanation
120 kV | 31 mAs | CTDIvol 34.29 mGy | ADMIRE

Courtesy of Hôpital Morges, Morges, Switzerland
Support stroke assessment with low kv imaging and zero-click thanks to Recon&GO
Native: 120kVp | CTDIvol 42 mGy – CTA 70kVp | CTDIvol 2.96 mGy – CT Perfusion 70kVp | CTDIvol 103 mGy

Courtesy of Hôpital Morges, Morges, Switzerland
Brain evaluation including spectral CTA of the cervical and cerebral vessels
CTA: 80 / Sn 140 kVp | CTDIvol 10.4 mGy Brain: 120 kVp | 40.4 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Visualization of iodine uptake with syngo.CT DE Brain Hemorrhage
TwinSpiral Dual Energy CT: 80/Sn150 KV | CTDIvol 37.06 mGy

Courtesy of University Hospital Erlangen, Erlangen, Germany
Ultra high-resolution inner ear without dose penalties thanks to Tin Filter
Sn130 kV | CTDIvol 24.07 mGy

Courtesy of Centro Hospitalar e Universitario de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Rule-out of bleeding and vascular status clarification
Native: 120 kVp | CTDIvol 38.4 mGy | CTA: 80kV | CTDIvol 6.3 mGy

Courtesy of Paras Hospitals, Panchkula, India
Penumbra assessment with volume perfusion CT
Native: 120 kV | CTDIvol 37 mGy | CT Perfusion: 70kV | CTDIvol 162 mGy

CT role in head emergency and stroke assessment
Automated support along the imaging pathway
syngo.CT Dynamic Angio and syngo.CT Neuro DSA are part of the medical device syngo.CT Applications. Trauma Layouts, Stroke Layout, and Parallel Ranges are part of the medical device syngo.CT Extended functionalities. The products mentioned here are not commercially available in all countries. Due to regulatory reasons, their future availability cannot be guaranteed.















Innovating in neuroradiology with photon-counting CT
Our breakthrough photon-counting technology enables a profound clinical impact beyond the reach of conventional CT. The NAEOTOM Alpha class lets you visualize anatomy and characterize materials in high detail while keeping dose low. Thanks to inherent spectral imaging and an ultra-thin slice thickness (up to just 0.2 mm), you can gain insight into details of the brain that may be inaccessible with conventional CT systems. Photon-counting technology offers increased resolution, inherently available spectral imaging options, better image quality, and improved dose efficiency, which together enable a change at the front line of stroke and neurological care.
Redefining imaging at the front line of stroke care
NAEOTOM Alpha has eclipsed conventional high-end CT scanners at the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Hear from Anke van der Eerden, MD, and the team how ultra-thin slice thickness has enabled a whole new level of detail while keeping dose to a minimum.
State-of-the-art stroke diagnosis and treatment
Discover the exciting possibilities that photon-counting CT offers for serving stroke patients in this talk by Aad van der Lugt, MD, from Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, Netherlands.
Delivering timely stroke diagnosis and care
For stroke patients, time is of the essence. Every minute saved can positively impact patient outcomes. That’s why it’s key to save time along the entire stroke pathway – from the onset of stroke to treatment and follow-up.
Transforming care delivery with Mobile Stroke Units
Mobile Stroke Units permit head CT imaging before patients even enter the hospital. Hear Johann Rink, MD, describe the real-life impact that installing an MSU has had on stroke care at Mannheim University Medical Centre in Mannheim, Germany.
At the nexus of treatment innovation: hybrid CT-angio systems
Implementing a hybrid interventional suite has reduced the door-to-groin time at Vall d’Hebron Hospital in Barcelona, Spain, to less than 30 minutes. Listen to Carlos Molina, MD, and Alejandro Tomaselli, MD, share their journey.
Improve ICU workflows with point-of-care imaging
Scanning patients directly in the ICU can avoid complications and improve efficiency. In this talk, Johan Wasselius, MD, explains how portable CT imaging with SOMATOM On.site has helped Skåne University Hospital, in Lund, Sweden, improve critical care workflows.
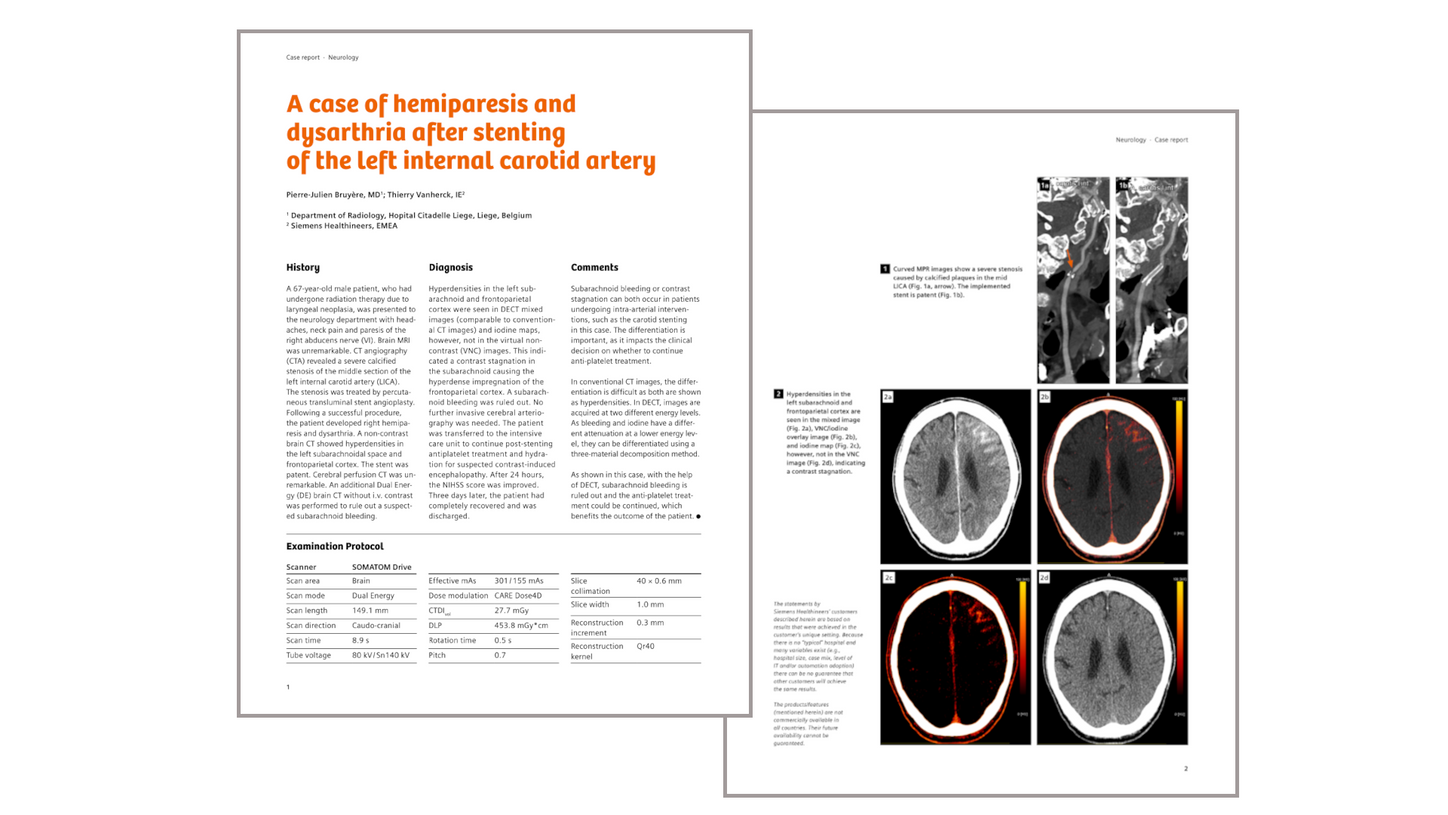
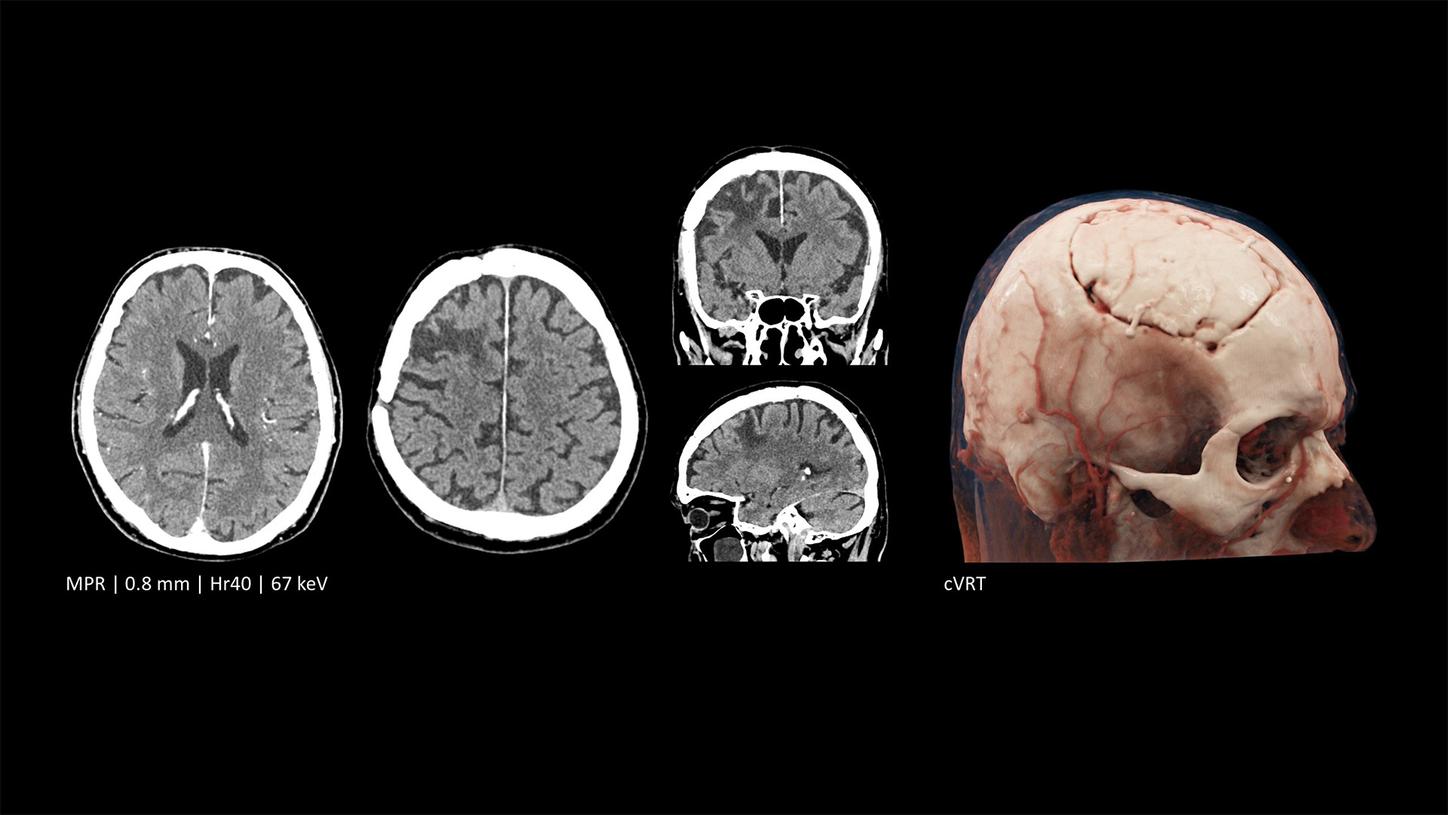
Clinical case: Differentiation between subarachnoid bleeding and contrast stagnation after carotid stenting
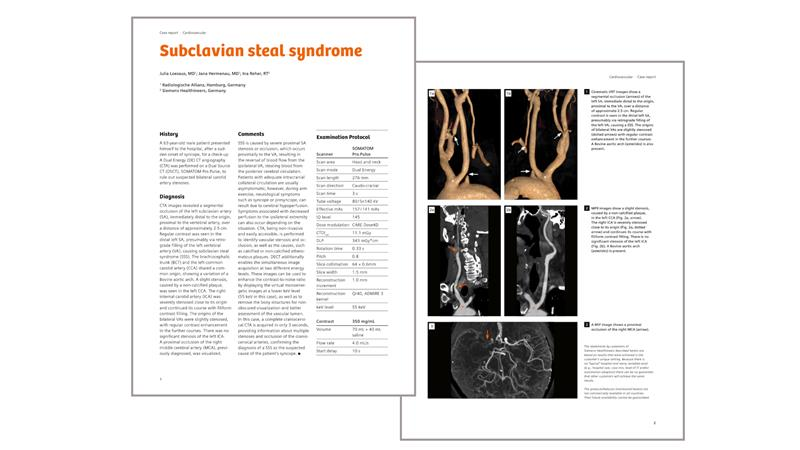
Clinical case: Diagnosis of subclavian steal syndrome after sudden onset of syncope
Did this information help you?
Thank you.
The statements by Siemens Healthineers’ customers described herein are based on results that were achieved in the customer's unique setting. Because there is no "typical" hospital and many variables exist (e.g., hospital size, case mix, level of IT and/or automation adoption) there can be no guarantee that other customers will achieve the same results.